Laser welding operates on the working principle of using a strong laser beam. This beam melts and joins materials, creating a tough connection. You control the laser by aiming it at the right spot, which helps you bond things quickly and precisely. The process generates a lot of heat in one small area, minimizing the bending of the metal. As a result, the welds appear neat and clean.
Laser welding allows you to position the weld accurately. You can also control how deep the weld penetrates, which means less heat is transferred to surrounding areas.
| Welding Method | Speed (inches per minute) |
|---|---|
| Laser Welding | > 200 |
| MIG Welding | 20-50 |
| Market Value (2025) | USD 2.9 billion |
| Market Forecast (2035) | USD 4.2 billion |
Key Takeaways
- Laser welding uses a focused laser beam. It melts and joins materials. This makes strong and precise welds.
- The process is faster than old welding methods. It finishes jobs in about 10 minutes. TIG welding takes about 90 minutes.
- Quality checks during welding are very important. Sensors and cameras help make sure welds are strong. They also help find defects.
- Pick the right welding method for your material. Use keyhole for thick materials. Use conduction for thin materials. This helps get the best results.
- Safety is very important. Always wear protective gear. Follow safety rules to stop accidents.
Working Principle of Laser Welding
Fusion Welding Principle
Laser welding uses fusion welding to join metal pieces. The laser beam melts the metals at the joint. This creates a strong bond. The heat is very intense and focused. The metals melt and form a small pool. This pool is liquid metal. Air cannot reach the molten pool. This keeps the weld clean and safe from dirt.
- Fusion welding makes a lot of heat at the joint. This melts the base metals in a small area.
- The melted metals form a pool. Heat keeps the pool liquid until the weld is done.
- The molten pool is protected from air. This stops dirt from getting in and keeps the weld strong.
- When the pool cools, the metals join together. Atoms mix and react, making a strong, smooth bond.
Scientists have tested laser welding in many experiments. They tried it on different metals and alloys. Some studies added special materials like Zr foil. This made the weld even stronger. Other tests showed laser welds can be as strong as 70% of the original metal. These results show fusion welding in laser welding makes tough and reliable joints.
| Study | Findings | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Gao et al. | Looked at the ‘blank zone’ in SiCp/Al fusion welded joints. | Fusion welding has a small process window because of bad phase formation. |
| Urena et al. | Tested AA2014/SiCp thin plates. Welds were 50% as strong as base metal. | Weakness came from phases at the joint. |
| Jian et al. | Studied uneven SiC spread during welding. | Tried to get welds with 70% of base metal strength. |
| Zhang et al. | Made a model for laser welding temperature and melt flow. | Studied how solid, liquid, and vapor interact. |
| Mi et al. | Added Zr foil to make the fusion zone harder. | Joint strength went up from 105.6 MPa to 234.7 MPa. |
| Ligen et al. | Did laser welding of SiCp/6061Al bars with alloying. | Stopped pin-like phases from forming. |
Many research articles show laser welding helps metals resist wear and corrosion. These studies prove laser welding makes strong and lasting joints for many uses.
Laser-Material Interaction
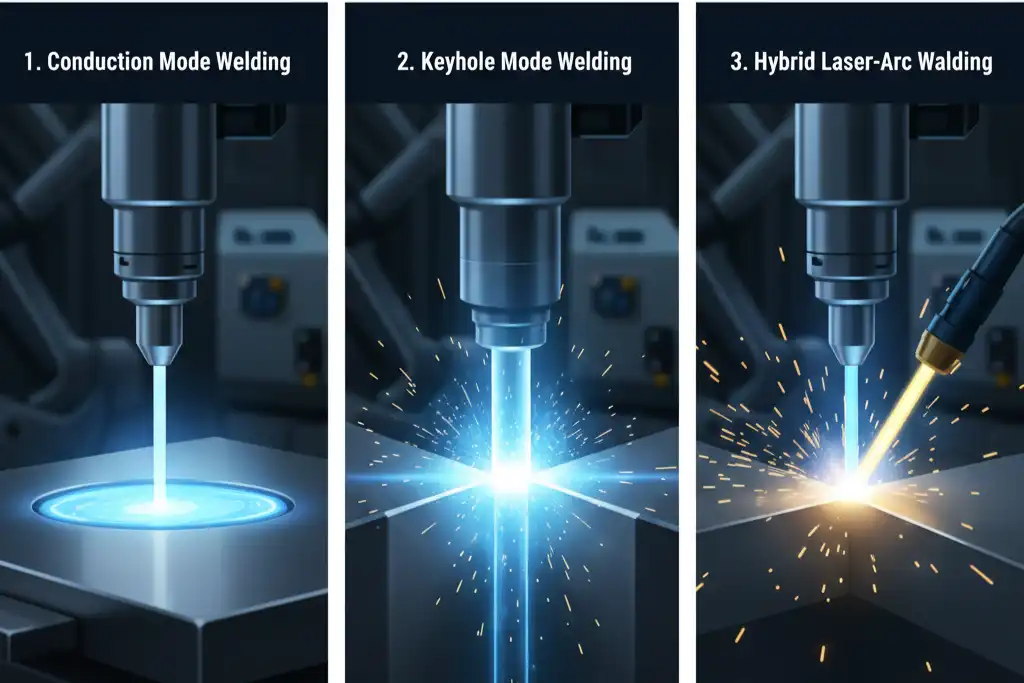
Laser welding works by how the laser beam hits the metal. The energy goes into the metal in two ways: conduction mode and keyhole mode. In conduction mode, heat spreads out. This makes a wide, shallow weld. In keyhole mode, the laser makes a deep, narrow hole. This gives a deeper weld.
How the laser works depends on many things. Power density, metal type, and air around the weld all matter. These things change how much energy the metal takes in. They also change the weld pool’s shape and quality. Sometimes, the process switches between conduction and keyhole modes. This depends on your settings and the metal you use.
Tip: You can change the laser’s power and focus. This lets you pick how deep and wide your weld is. You can get the results you want for each project.
Laser welding is different from old welding methods. It is much faster and causes less bending. You can finish a weld in 10 minutes. TIG welding can take 90 minutes for the same job. The laser beam is focused and small. This means less metal bends or warps. Cleaning up after welding is easier. There is less soot to remove.
| Aspect | Laser Welding | Traditional TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Welding time drops from 90 to 10 minutes per part | Slower, 90 minutes per part |
| Heat Input | Much higher heat density | Big heat-affected zone (HAZ) |
| Distortion | Very little bending or warping | More bending from arc |
| Post-welding Work | Less soot, easy cleaning | More cleaning needed |
Laser welding gives you control, speed, and clean welds. You can use these benefits to make better projects and get great results every time.
Basic Process Steps
Equipment Setup
You start laser welding by preparing your workspace. Make sure the area is clean, bright, and free from anything that can catch fire. Put on your gloves and goggles, and check that the room has good airflow. If you use welding wire, pick the right type for your metal. Safety matters, so you need to follow rules and standards.
| Safety Standard/Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| Nominal Hazard Zone (NHZ) | Check the area for laser risks and decide what protection you need. |
| Training for Adjacent Staff | Teach everyone near the laser about safety steps. |
| Barrier Zones | Mark areas to keep people away from danger. |
| PPE Education | Show how to use gloves, goggles, and other gear. |
| Equipment Inspections | Check machines often to keep them safe. |
| Warning Signs | Put up signs to warn about laser hazards. |
| Access Control Measures | Only let trained people into the laser area. |
Tip: Always follow ANSI Z136 guidelines for safe use of lasers in your workspace.
Operation & Control
You control the laser welding process by setting up your machine and parts. Make sure the metal pieces fit together with no gaps. Use clamps to hold everything in place. You do not need filler materials for most laser welds, which makes the process clean and fast. You can weld metals and thermoplastics with this method.
To get strong welds, you need to watch the process closely. Use sensors and cameras to check the weld as it happens. Adjust the laser’s power and speed to match your project. Shielding gas helps keep the weld clean. You can change the gas type and flow to get the best results.
- Prepare joints and surfaces before welding.
- Use real-time monitoring to spot problems early.
- Test and adjust shielding gas for better welds.
- Clamp parts tightly to avoid bending.
Quality Monitoring
You keep welds strong by checking quality during and after welding. Use high-speed cameras and sensors to watch the weld pool. Pyrometers measure temperature, and vision systems check for color changes or thin spots. You can use sound sensors to find cracks or defects.
If you see problems like spatter, cracks, or porosity, you can fix them by cleaning surfaces, changing laser settings, or adjusting speed. X-ray images help you find hidden defects inside the weld. Machine learning tools can sort good welds from bad ones quickly.
Note: Quality monitoring helps you follow the working principle of laser welding and ensures every weld meets your standards.
Types of Laser Welding
Laser welding has two main methods. These are keyhole welding and heat conduction welding. You pick the best one by knowing how each works.
Keyhole Welding
Keyhole welding uses a strong laser beam. The laser melts metal fast and makes a deep hole called a keyhole. This method is good for thick materials. It makes a strong weld that can handle lots of stress. The laser goes deep into the metal. The weld pool gets very hot, up to 2000°F. This makes a joint that stays strong under heavy loads.
Keyhole welding helps stop cracks and breaks. You see it used in cars and airplanes. It is great for parts that need to be tough.
Tip: Pick keyhole welding for thick metals. Use it when you need a joint that will not break under pressure.
Heat Conduction Welding
Heat conduction welding works in another way. The laser spreads heat over the surface. It does not make a deep hole. You get a wide, shallow weld. This method uses less energy. The temperature stays lower. It is best for thin materials. You get a smooth and neat finish.
This method is good for electronics and medical tools. It works well for thin metal sheets. The welds look clean. There is less chance of burning the metal.
Here is a table that shows the main differences:
| Feature | Keyhole Welding | Conduction Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Depth | Deep and narrow | Shallow and wide |
| Energy Usage | High laser energy | Lower laser energy |
| Weld Pool Temperature | Higher temperatures, can reach 2000°F | Lower temperatures, around 2000°F |
| Aspect Ratio | Typically ranges from 0.5 to 2.5 | Not applicable |
| Material Thickness | Can weld thick materials up to 25mm | Limited to thinner materials |
| Joint Strength | Strong joints that handle high stress | Generally less strong than keyhole |
Keyhole welding gives deeper and stronger welds. Conduction welding is better for thin and delicate parts. Pick the method that fits your project needs.
System Components & Process Factors
Laser Source & Delivery
You need the right equipment to follow the working principle of laser welding. The main parts include the laser source, the delivery system, and the controls. You can choose from several types of lasers for your welding projects:
- Direct-diode lasers work fast and fit in small spaces. You see them in automotive and electronics work.
- Fiber lasers give you high power and a sharp beam. These lasers help you weld with great accuracy in aerospace and electronics.
- Gas lasers, like CO2 lasers, cut and weld many materials. You often find them in car factories.
The delivery system moves the laser beam to the weld spot. The quality of this system affects how well and how fast you weld. Here is a table that shows how delivery systems change your results:
| Factor | Impact on Welding Process |
|---|---|
| Welding Speed | Good delivery lets you weld faster and finish jobs quickly. |
| Accuracy and Precision | Sharp beams help you control the weld spot size for high standards. |
| Material Utilization | Focused beams keep heat small, saving material and money. |
| Equipment Efficiency | Efficient delivery boosts output and cuts down on mistakes. |
Tip: Pick a laser and delivery system that match your project needs. This helps you get strong, clean welds every time.
Material & Joint Design
You must know your material before you start welding. Each metal acts differently under the laser. Here is a table that shows what matters most for each type:
| Material | Critical Properties | What This Means for Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Needs high energy, welds fast, low bending | Strong welds, good for big jobs |
| Alloy Steel | Deep welds, keeps shape under heat | Tough joints, less overheating |
| Stainless Steel | Fights rust, stays strong when hot | Clean welds, less bending |
| Copper | Moves heat fast, hard to weld | Needs focused energy, watch heat buildup |
| Aluminum | Reflects light, melts easy | Use high power, clean surface first |
Joint design also matters. The way you shape and place the weld changes how strong it is. Research shows that the pattern of the weld can make it up to three times stronger. For example, a C-shape weld can handle more force than a straight line. You should pick a joint design that fits your project and makes the weld last longer.
Process Parameters
You control many settings during laser welding. These settings change how the weld looks and how strong it is. Important process parameters include:
- Focus position changes how deep the laser goes.
- Welding speed affects how much heat you use.
- Pulse energy and frequency control weld quality.
- Protective gas keeps the weld clean and stable.
- Surface cleanliness stops defects.
- Fixturing holds parts steady.
You must watch for problems like porosity, spatter, or cracks. Cleaning the surface and adjusting the laser power can fix many issues. Cooling rates also matter. Fast cooling can make steel harder, while slow cooling keeps it tough. Here is a table with good settings for common materials:
| Material | Power Settings | Speed Range (m/min) | Shielding Gas Flow (L/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Moderate | Up to 10 | 10-20 |
| Aluminum | High Power | 1-5 | 20-30 |
| Brass/Copper | High Power (Fiber/Green) | N/A | N/A |
Note: Always test your settings before starting a big job. This helps you follow the working principle and get the best results.
Advantages, Limitations, Applications
Benefits of Laser Welding
Laser welding helps you work faster than old welding. You get neat welds with less waste. Machines do most of the work, so you save time. Laser welding fits well in automated lines. You spend less time setting up and more time making things.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High-speed welding | Laser welding is 4-5 times faster than old ways. You finish jobs quickly. |
| Integration with automation | It works with robots and machines. This means less setup and more work done. |
| Precision and accuracy | Welds are very exact. You do not need much fixing after. This saves money. |
| Reduced material waste | You use only what you need. There is little scrap left over. |
| Lower maintenance costs | The laser does not touch the metal. This means less fixing and cleaning. |
Laser welding saves you money. You use less power and fewer supplies. Machines do most jobs, so you need fewer workers. You finish projects fast and deliver on time.
Laser welding can be 10 times faster than TIG welding. This speed helps you meet market needs quickly.
Common Limitations
Laser welding has some problems you should know. You must watch the beam and heat to stop bad welds. Safety is important because lasers can hurt your skin or eyes. You need trained people to run the machines.
- Bad beam quality can make weak welds.
- Shiny metals like copper are hard to weld.
- Thick metals need stronger lasers or more passes.
- You must check and fix your machines often.
- The equipment and training cost a lot at first.
- Joints must fit well to stop mistakes.
You must get your materials ready and line them up right. Wrong settings or bad alignment can hurt your welds or tools.
Industrial Uses
Laser welding is used in many fields. Car makers use it for engines and batteries. Medical companies use it for implants and small metal parts. Airplane builders use it for tanks and body pieces. Electronics makers use it for tiny parts.
- Automotive Industry: Welds engine parts and battery contacts.
- Medical Industry: Joins implants and thin metal tools.
- Aerospace Industry: Makes fuel tanks and body panels.
- Electronics Industry: Builds circuit boards and sensors.
Laser welding helps car makers build better batteries and lighter cars. You see its effect in new designs and better performance.
You start laser welding by getting the materials ready. Next, you point the laser at the joint. The laser melts the metal where you want to join it. Shielding gas is used to keep the weld safe from air. This method is fast and makes deep, exact welds.
| Key Feature | Benefit for You |
|---|---|
| High Energy Density | Welds are quick and strong |
| Pinpoint Precision | Joints are neat and exact |
| Low Heat Input | Metal bends less |
Think about what kind of material you have. Check the laser’s power and how you will cool things down. Try new tools like AI and fiber lasers to get better welds. The American Welding Society has rules and tips to help you learn more.
FAQ
What safety steps should you follow during laser welding?
You need to wear goggles and gloves. Always look for dangers in your workspace. Put up warning signs and use barriers to keep people safe.
Tip: Always follow ANSI Z136 rules when using lasers.
Which materials can you weld with a laser?
Lasers can weld steel, aluminum, copper, and some thermoplastics.
| Material | Weldability |
|---|---|
| Steel | Excellent |
| Aluminum | Good |
| Copper | Moderate |
| Thermoplastics | Possible |
How does laser welding compare to traditional welding in cost?
Laser welding costs more at first because of the machines. Over time, you save money because it works faster and wastes less material.
- First cost: High
- Savings later: Big
Can you automate laser welding?
You can use robots and sensors to automate laser welding. Automation helps you make accurate welds and finish jobs faster.
Note: You must check automated systems often to keep welds good.
See also
How to determine if a laser cleaning machine is worth buying
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating ROI for Laser Cleaning
Comparison of efficiency between laser cleaning and manual polishing
How to Adjust Galvanometer Scanning Speed for Superior Cleaning